You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
Gitlab Authenticator
Guard installation guide can be found here. To use Gitlab, you need a client cert with Organization set to Gitlab. To ease this process, use the Guard cli to issue a client cert/key pair.
$ guard init client {common-name} -o Gitlab
Deploy Guard Server
To generate installer YAMLs for guard server you can use the following command.
$ guard get installer \
--auth-providers="gitlab" \
> installer.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f installer.yaml
Additional flags for gitlab:
# Base url for GitLab, keep empty to use default gitlab base url
--gitlab.base-url=<base_url>
# Use group ID for authentication instead of group full path (default: false)
--gitlab.use-group-id
The GitLab base-url needs to include the path to the API. For example
https://<base-url>/api/v4
Please note that, since 0.3.0 release, Guard server will return group full path as groups in UserInfo. This will cahnge how subgroups are returned in UserInfo. Also note that, group names are not stable and editable in Gitlab. To returns group ids (stable) in UserInfo, set --gitlab.use-group-id=true in guard server binary.
$ guard get installer \
--auth-providers="gitlab" \
--gitlab.use-group-id=true \
> installer.yaml
Issue Token
To use Gitlab authentication, you can use your personal access token with scope api. You can use the following command to issue a token:
$ guard get token -o gitlab
Guard uses the token found in TokenReview request object to read user’s profile information and list of groups this user is member of. In the TokenReview response, status.user.username is set to user’s Gitlab login, status.user.groups is set to the list of the groups where this user is a member.
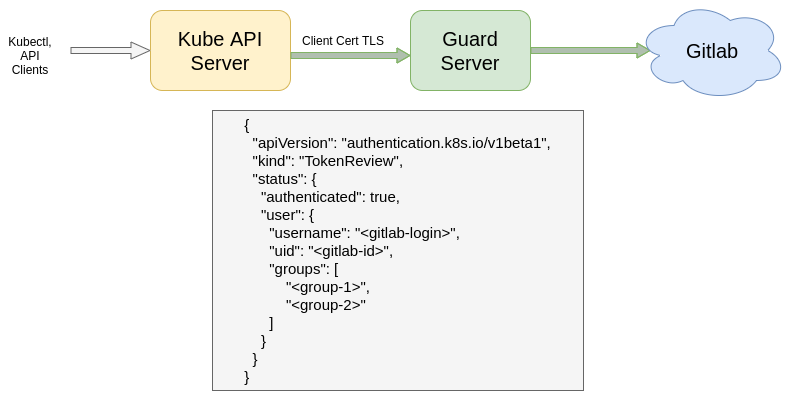
{
"apiVersion": "authentication.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "TokenReview",
"status": {
"authenticated": true,
"user": {
"username": "<gitlab-login>",
"uid": "<gitlab-id>",
"groups": [
"<group-1>",
"<group-2>"
]
}
}
}
Configure Kubectl
kubectl config set-credentials <user_name> --token=<token>
Or You can add user in .kube/confg file
...
users:
- name: <user_name>
user:
token: <token>
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces --user <user_name>
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system etcd-minikube 1/1 Running 0 7h
kube-system kube-addon-manager-minikube 1/1 Running 0 7h
kube-system kube-apiserver-minikube 1/1 Running 1 7h
kube-system kube-controller-manager-minikube 1/1 Running 0 7h
kube-system kube-dns-6f4fd4bdf-f7csh 3/3 Running 0 7h








